GPG management is an essential component in securing digital communications and ensuring data privacy. In today's fast-paced digital landscape, safeguarding sensitive information has become a top priority for individuals and organizations alike. GPG, or GNU Privacy Guard, offers robust encryption standards that serve as a trusted solution for protecting data against unauthorized access. By understanding and implementing effective GPG management strategies, users can enhance their security posture and maintain confidentiality in their communications.
As cyber threats continue to evolve, the importance of GPG management cannot be overstated. With the rise of sophisticated hacking techniques and data breaches, the need for reliable encryption methods has become more pressing. GPG provides users with the tools to encrypt, decrypt, and sign data, ensuring that only intended recipients can access the information. Moreover, GPG management involves a set of practices that help users effectively create, distribute, and revoke keys, making it a critical aspect of cybersecurity.
In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the intricacies of GPG management, exploring its significance, best practices, and the steps necessary to ensure optimal security. From key generation to key revocation, each aspect of GPG management plays a vital role in maintaining data integrity. Whether you're a seasoned professional or new to encryption, this guide will equip you with the knowledge needed to navigate the complexities of GPG management with confidence. Let's embark on a journey to enhance your understanding and application of GPG management principles.
Table of Contents
- What is GPG Management?
- Why is GPG Management Important?
- How to Generate GPG Keys?
- GPG Key Distribution: Best Practices
- Managing the GPG Key Lifecycle
- What is GPG Signing and Verification?
- GPG Key Revocation: When and How?
- Top Tools for GPG Management
- Implementing GPG Management in Organizations
- Common Challenges in GPG Management
- Best Practices for Effective GPG Management
- The Future of GPG Management
- Case Studies: Successful GPG Management
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion
What is GPG Management?
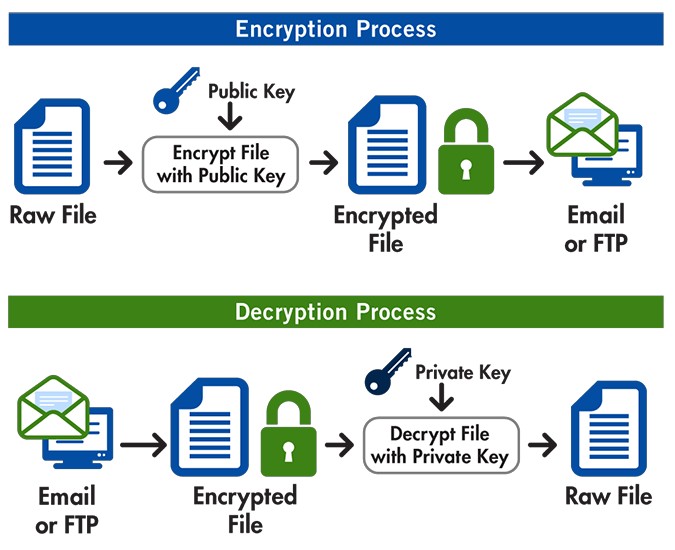
GPG management refers to the comprehensive process of handling and maintaining GNU Privacy Guard (GPG) keys for encryption and decryption purposes. GPG is a popular open-source encryption tool that allows users to secure their digital communications by encrypting messages and files, thereby ensuring only authorized individuals can access the data. The management aspect involves generating, distributing, and revoking keys, as well as signing data to verify its authenticity.
In essence, GPG management provides a framework for ensuring data privacy and integrity in digital communications. It encompasses a range of activities, including:
- Generating and storing cryptographic keys securely
- Distributing public keys to intended recipients
- Revoking keys when they are compromised or no longer needed
- Signing data to authenticate the sender's identity
Effective GPG management is crucial for both individuals and organizations looking to protect sensitive information. By implementing robust GPG practices, users can mitigate the risk of data breaches and unauthorized access, thereby maintaining the confidentiality and integrity of their communications.
Why is GPG Management Important?
In today's digital age, the importance of GPG management cannot be overstated. As cyber threats become increasingly sophisticated, ensuring data privacy and security has become a top priority for individuals and businesses alike. GPG management provides a reliable framework for safeguarding sensitive information against unauthorized access and data breaches.
Several key factors underscore the importance of GPG management:
- Data Privacy: GPG encryption ensures that only intended recipients can access sensitive data, protecting it from unauthorized access.
- Data Integrity: By signing data, GPG management helps verify the authenticity and integrity of the information, ensuring it has not been tampered with.
- Compliance: Many industries are subject to strict data protection regulations. Implementing effective GPG management can help organizations comply with these requirements, avoiding potential legal and financial repercussions.
- Trust: By using GPG management to sign and encrypt communications, users can build trust with their counterparts, knowing that their data is secure.
Ultimately, GPG management serves as a cornerstone of a robust cybersecurity strategy, helping users protect their digital communications and maintain data privacy in an increasingly interconnected world.
How to Generate GPG Keys?
Generating GPG keys is a fundamental step in the GPG management process. These cryptographic keys are used to encrypt, decrypt, and sign data, ensuring secure communication. The process involves creating a pair of keys: a public key, which can be shared with others, and a private key, which must be kept confidential.
Here's a step-by-step guide to generating GPG keys:
- Install GPG Software: Ensure you have GPG software installed on your system. You can download it from the official GNU Privacy Guard website.
- Open Terminal: Use a terminal or command prompt to access the GPG command line interface.
- Generate Key Pair: Enter the command
gpg --full-generate-keyto start the key generation process. - Select Key Type: Choose the type of key you want to generate (e.g., RSA and RSA, DSA and Elgamal).
- Set Key Length: Specify the key length, typically 2048 or 4096 bits for enhanced security.
- Set Expiration Date: Choose an expiration date for the key or opt for no expiration.
- Enter User Information: Provide your name, email address, and an optional comment to associate with the key.
- Create Passphrase: Set a strong passphrase to protect your private key.
- Key Generation Complete: Once the process is complete, you'll have a public key (to share) and a private key (to keep secure).
By following these steps, you can generate GPG keys and begin using them to secure your digital communications. Remember to keep your private key and passphrase confidential to maintain the integrity of your encryption.
GPG Key Distribution: Best Practices
Distributing GPG keys effectively is a critical aspect of GPG management. The public key must be shared with intended recipients so they can encrypt messages or verify signatures. However, it's important to distribute keys securely to prevent unauthorized access.
Here are some best practices for distributing GPG keys:
- Use Secure Channels: Share your public key through secure channels, such as encrypted email or secure file transfer services, to prevent interception by malicious actors.
- Verify Key Authenticity: Ensure recipients can verify the authenticity of your public key. This can be done through key fingerprint verification or using a trusted key server.
- Key Servers: Upload your public key to a trusted key server, allowing others to download and verify it easily. Popular key servers include the MIT PGP Public Key Server and the Ubuntu Key Server.
- Revocation Certificates: Provide recipients with a revocation certificate in case your key needs to be revoked in the future. This ensures they can update their records promptly.
Following these practices helps ensure that your public key is distributed securely and can be trusted by recipients. Proper key distribution is crucial for maintaining the integrity of your encrypted communications.
Managing the GPG Key Lifecycle
The GPG key lifecycle encompasses the creation, usage, and eventual revocation of cryptographic keys. Proper management of this lifecycle is essential for maintaining the effectiveness of your encryption strategy and ensuring the security of your communications.
The key lifecycle consists of several stages:
- Key Generation: Creating a new pair of public and private keys using secure methods.
- Key Usage: Using the keys to encrypt, decrypt, and sign data. It's important to use keys responsibly and ensure they are not exposed to unauthorized users.
- Key Renewal: Periodically renewing keys to maintain their security. This involves generating a new key pair and securely distributing the new public key to recipients.
- Key Revocation: Revoking keys when they are compromised or no longer needed. This ensures that old keys cannot be used to decrypt or sign data.
- Key Archival: Securely storing old keys for archival purposes, in case they are needed for verification or legal compliance.
Managing the GPG key lifecycle effectively helps ensure that your encryption strategy remains robust and that your communications remain secure. By adhering to best practices, you can mitigate the risk of key compromise and maintain the integrity of your data.
What is GPG Signing and Verification?
GPG signing and verification are integral components of the GPG management process, ensuring the authenticity and integrity of digital communications. Signing data allows the sender to prove their identity, while verification enables the recipient to confirm the data's origin and integrity.
Here's how GPG signing and verification work:
- Signing Data: The sender uses their private key to create a digital signature for the data. This signature is unique to the sender and the specific data being signed.
- Sending Signed Data: The signed data, along with the sender's public key, is sent to the recipient.
- Verification Process: The recipient uses the sender's public key to verify the digital signature. If the signature is valid, it confirms that the data has not been tampered with and originates from the claimed sender.
GPG signing and verification provide a high level of trust in digital communications, allowing users to authenticate the sender's identity and ensure data integrity. This process is particularly important in environments where data authenticity is critical, such as in financial transactions or legal communications.
GPG Key Revocation: When and How?
GPG key revocation is a crucial aspect of GPG management, involving the invalidation of a cryptographic key when it is no longer secure or needed. Revocation ensures that compromised or obsolete keys cannot be used to decrypt or sign data, maintaining the security of the encrypted communications.
There are several reasons why a GPG key might need to be revoked:
- Key Compromise: If a private key is exposed to unauthorized users, it must be revoked immediately to prevent misuse.
- Expiration: Keys that have reached their expiration date should be revoked and replaced with new ones.
- Key Replacement: When a key is replaced with a new key pair, the old key should be revoked to prevent its continued use.
Here's how to revoke a GPG key:
- Create a Revocation Certificate: Use the command
gpg --gen-revoke [key-id]to generate a revocation certificate for the key. - Distribute Revocation Certificate: Share the revocation certificate with key servers and recipients to inform them that the key is no longer valid.
- Update Key Servers: Upload the revocation certificate to key servers to ensure that others can download the updated status of the key.
By following these steps, you can effectively revoke a GPG key, ensuring that it cannot be used for unauthorized purposes. Proper key revocation is essential for maintaining the security and integrity of your encrypted communications.
Top Tools for GPG Management
Several tools and software solutions are available to facilitate GPG management, providing users with the capabilities to generate, distribute, and revoke keys, as well as sign and verify data. These tools simplify the GPG management process, making it more accessible and efficient for users.
Here are some of the top tools for GPG management:
- GnuPG (GNU Privacy Guard): The official and most widely used GPG software, offering a comprehensive set of features for managing keys and encrypting data.
- Kleopatra: A graphical user interface for GPG, providing an easy-to-use platform for key generation, signing, and encryption.
- Seahorse: Another graphical interface for managing GPG keys, integrated with the GNOME desktop environment.
- Mailvelope: A browser extension that enables GPG encryption and signing for web-based email platforms like Gmail and Outlook.
- Gpg4win: A Windows-based suite of tools for GPG management, including GnuPG, Kleopatra, and other utilities.
These tools offer a range of features to support effective GPG management, catering to different user needs and preferences. By utilizing these tools, users can streamline their GPG management processes and enhance their data security.
Implementing GPG Management in Organizations
For organizations, GPG management is a critical component of a comprehensive cybersecurity strategy. Implementing GPG management practices can help organizations protect sensitive data, ensure compliance with regulations, and build trust with clients and partners.
Here are some key steps for implementing GPG management in organizations:
- Develop a Policy: Establish a clear policy outlining the organization's approach to GPG management, including key generation, distribution, and revocation procedures.
- Training and Awareness: Provide training to employees on the importance of GPG management and how to use GPG tools effectively.
- Centralized Key Management: Implement a centralized system for managing and distributing keys, ensuring that all employees have access to the necessary public keys.
- Regular Audits: Conduct regular audits of the organization's GPG management practices to identify and address any vulnerabilities or areas for improvement.
- Compliance and Monitoring: Ensure that the organization's GPG management practices comply with industry regulations and standards, and monitor key usage to detect any anomalies.
By adopting these practices, organizations can enhance their data security, mitigate the risk of data breaches, and maintain the integrity of their communications. Effective GPG management is essential for protecting sensitive information and maintaining trust in digital interactions.
Common Challenges in GPG Management
While GPG management offers numerous benefits for data security, it also presents several challenges that users must navigate. Understanding and addressing these challenges is crucial for maintaining the effectiveness of GPG management practices.
Some common challenges in GPG management include:
- Complexity: The technical nature of GPG can be intimidating for users, leading to potential errors in key generation, distribution, or revocation.
- User Adoption: Ensuring widespread adoption and correct usage of GPG tools within an organization can be challenging, particularly if employees are unfamiliar with encryption practices.
- Key Management: Managing a large number of keys can be cumbersome, especially for organizations with numerous employees and external partners.
- Key Compromise: The risk of key compromise, either through hacking or human error, poses a significant threat to data security.
To overcome these challenges, users and organizations must invest in training, adopt user-friendly tools, and establish robust key management policies. By doing so, they can enhance their GPG management practices and ensure the security of their digital communications.
Best Practices for Effective GPG Management
Implementing best practices for GPG management is essential for ensuring the security and integrity of encrypted communications. By following these guidelines, users can enhance their data protection efforts and minimize the risk of unauthorized access.
Here are some best practices for effective GPG management:
- Use Strong Passphrases: Protect your private key with a strong, unique passphrase to prevent unauthorized access.
- Regular Key Renewal: Periodically renew your keys to ensure they remain secure and effective.
- Secure Key Storage: Store private keys in a secure location, such as a hardware security module or encrypted storage device.
- Verify Key Authenticity: Always verify the authenticity of public keys before using them for encryption or verification purposes.
- Monitor Key Usage: Regularly monitor key usage to detect any unauthorized activities or anomalies.
- Conduct Security Audits: Perform regular security audits of your GPG management practices to identify and address potential vulnerabilities.
By adhering to these best practices, users can strengthen their GPG management strategies and protect their digital communications from unauthorized access and data breaches.
The Future of GPG Management
As the digital landscape continues to evolve, the role of GPG management in ensuring data security is expected to grow in importance. Emerging technologies and trends will shape the future of GPG management, influencing how users and organizations approach data protection.
Several developments are likely to impact the future of GPG management:
- Advancements in Cryptography: New cryptographic algorithms and techniques may enhance the security and efficiency of GPG management.
- Integration with Emerging Technologies: Integration with technologies like blockchain and quantum computing could offer new opportunities for securing digital communications.
- Increased Regulatory Requirements: As data protection regulations become more stringent, organizations will need to prioritize GPG management to ensure compliance.
- User-Friendly Solutions: The development of more intuitive and accessible GPG management tools will drive greater adoption and usage.
By staying informed about these trends and embracing new technologies, users and organizations can ensure that their GPG management practices remain effective and relevant in the face of evolving cybersecurity challenges.
Case Studies: Successful GPG Management
Examining case studies of successful GPG management provides valuable insights into the practical application of GPG practices and the benefits they offer for data security. These real-world examples highlight how individuals and organizations have effectively implemented GPG management to protect their digital communications.
Here are a few notable case studies:
- Case Study 1: A multinational corporation implemented GPG management to secure its internal communications, resulting in a significant reduction in data breaches and increased trust from clients and partners.
- Case Study 2: A non-profit organization adopted GPG management to protect sensitive donor information, ensuring compliance with data protection regulations and enhancing donor confidence.
- Case Study 3: An individual journalist used GPG management to secure communications with confidential sources, maintaining the integrity and confidentiality of sensitive information.
These case studies demonstrate the effectiveness of GPG management in enhancing data security and protecting sensitive information. By learning from these examples, users and organizations can apply similar strategies to their own GPG management practices.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some frequently asked questions about GPG management:
- What is the difference between GPG and PGP?
GPG (GNU Privacy Guard) is a free and open-source implementation of the PGP (Pretty Good Privacy) encryption standard. While both serve similar purposes, GPG is widely used due to its open-source nature.
- Can GPG be used for encrypting emails?
Yes, GPG can be used to encrypt emails, ensuring that only intended recipients can read the content. Many email clients support GPG encryption through plugins or extensions.
- How do I verify a GPG signature?
To verify a GPG signature, you need the sender's public key. Use the command
gpg --verify [signature-file] [data-file]to confirm the authenticity and integrity of the signed data. - What happens if I lose my GPG private key?
If you lose your GPG private key, you will be unable to decrypt any data encrypted with your public key. It's important to securely back up your private key to prevent data loss.
- How do I revoke a GPG key?
To revoke a GPG key, generate a revocation certificate using the command
gpg --gen-revoke [key-id]and distribute it to key servers and recipients. - Is GPG management suitable for small businesses?
Yes, GPG management is suitable for businesses of all sizes, including small businesses. It provides an effective way to secure communications and protect sensitive information.
Conclusion
In conclusion, GPG management plays a vital role in securing digital communications and ensuring data privacy. By implementing effective GPG management practices, individuals and organizations can protect their sensitive information, build trust in their communications, and comply with data protection regulations. As the digital landscape continues to evolve, staying informed about emerging trends and technologies will be key to maintaining robust GPG management strategies. Whether you're an individual user or part of an organization, embracing GPG management is a crucial step toward safeguarding your digital interactions in an increasingly interconnected world.
You Might Also Like
Mastering The Savita Ingredient: A Culinary Game-ChangerStreator YMCA: A Community Hub For Health And Wellness
Inspiring Achievements Of Maureen Davis: Stories Of Success
In-Depth Look At Kroger Lithonia: A Community Staple
Alhambra AESD: A Comprehensive Guide To Education Dynamics
Article Recommendations
- Does Gizelle Bryant Have Siblings An Indepth Look In 2024
- Bluebay Grand Esmeralda
- Exploring Vegamovies A Comprehensive Guide For 2024